Create shell script
touch trunk.sh
Add the content to the script
#!/bin/bash
serviceIsRunning=false
var1=$(/usr/sbin/asterisk -rx "sip show peers" |grep trunk_name |awk '{print $6}'| sed 2,2d)
var2=$(echo $data | awk '{print $2}')
if [ "$var1" == OK ]
then
serviceIsRunning=true
echo "0:200:running"
fi
if [ $serviceIsRunning == false ]
then
echo "2:404:UNREACHABLE"
fi
Save the script and make it executable
chmod +x trunk.sh
Try to run it
./trunk.sh
Go to the PRTG, and add the SSH Script sensor to the device
In the «Script» field choose trunk.sh and SAVE
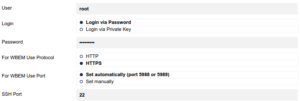
! Make sure your PRTG Server has access to Asterisk Server, if not, add root username and password
to the credentials in the BASIC DEVICE SETTINGS
Check network:
# ifconfig
lo Link encap:Local Loopback
inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0
inet6 addr: ::1/128 Scope:Host
UP LOOPBACK RUNNING MTU:16436 Metric:1
RX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:0
RX bytes:0 (0.0 b) TX bytes:0 (0.0 b)
Try to start Eth0 device
# ifup eth0
Device eth0 does not seem to be present, delaying initialisation
To Solve this :
Delete networking interface rules file so that it can be regenerated and reboot your CentOS system.
# rm /etc/udev/rules.d/70-persistent-net.rules
# reboot
New Mac address has been generated:
# This file was automatically generated by the /lib/udev/write_net_rules
# program, run by the persistent-net-generator.rules rules file.
#
# You can modify it, as long as you keep each rule on a single
# line, and change only the value of the NAME= key.
# PCI device 0x8086:0x100e (e1000)
SUBSYSTEM=="net", ACTION=="add", DRIVERS=="?*", ATTR{address}=="08:00:27:fe:c1:03", ATTR{type}=="1", KERNEL=="eth*", NAME="eth0"
Now edit /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0,
Add new HWADDR generated or remove it
Remove UUID line
Restart the networking service
# service network restart
Shutting down interface eth0: [ OK ]
Shutting down loopback interface: [ OK ]
Bringing up loopback interface: [ OK ]
Bringing up interface eth0: Determining if ip address 192.168.1.99 is already in use for device eth0...
[ OK ]
# ifconfig
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 08:00:27:FE:C1:03
inet addr:192.168.1.99 Bcast:xxxxxxxx Mask:255.255.255.0
inet6 addr: fe80::a00:27ff:fefe:c103/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:4400 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:129 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:387597 (378.5 KiB) TX bytes:19567 (19.1 KiB)
Enjoy!
sudo yum install httpd
sudo /usr/bin/mysql_secure_installation
By default, a MySQL installation has an anonymous user, allowing anyone
to log into MySQL without having to have a user account created for
them. This is intended only for testing, and to make the installation
go a bit smoother. You should remove them before moving into a
Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] y
... Success!
Normally, root should only be allowed to connect from 'localhost'. This
ensures that someone cannot guess at the root password from the network.
Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] y
... Success!
By default, MySQL comes with a database named 'test' that anyone can
access. This is also intended only for testing, and should be removed
before moving into a production environment.
Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] y
- Dropping test database...
... Success!
- Removing privileges on test database...
... Success!
Reloading the privilege tables will ensure that all changes made so far
will take effect immediately.
Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] y
... Success!
Cleaning up...
All done! If you've completed all of the above steps, your MySQL
installation should now be secure.
Thanks for using MySQL!
sudo yum install php php-mysql
sudo chkconfig httpd on sudo chkconfig mysqld on
sudo service httpd restart
yum install mysql mysql-server -y
service mysqld start
To enable SNMP on CentOS
yum install net-snmp-utils -y
yum install net-snmp -y
mv /etc/snmp/snmpd.conf /etc/snmp/snmpd.conf.org
vi /etc/snmp/snmpd.conf
rocommunity public
Save and Exit
/etc/init.d/snmpd start
chkconfig snmpd on
Make sure you configured your Firewall